You’ve probably seen a lot of foam in your time. But what is polyurethane foam? It’s known by many names and is one of those things we take for granted – or ignore – every time we open a parcel or sit on a chair.
But you might be surprised just how many variations of polyurethane foam there are, as well as how it’s made. So here’s the quick summary, then we’ll get into more details…
The term polyurethane is also called PU, Urethane, or Reflex foam. It covers a range of foams that are synthesized using polyol and isocyanate. It is an open-cell foam, generally of medium to low quality, with a shorter lifespan than other foams, but a wide variety of uses.
Closed-cell polyurethane foam is also available (often more commonly known as Polyethylene) and also used for a wide variety of purposes. You can get a better idea of this by reading my article on closed-cell foam.
Open-cell polyurethane foam has a number of pros, cons, and features associated with it. Here’s a list of what you can expect from polyurethane foam:
- Less-expensive
- Low to medium quality
- Low to medium density
- Soft texture and reasonably firm support
- Generally a shorter life span than other foams
- Fewer certifications
What is polyurethane foam – background
Polyurethane foam is a member of the leading wide-ranging and highly diverse family of “Polymers” or “plastics”. Polyurethane comes in two main forms; “closed” or “open: cellular structure.
It’s this (mostly) open-cell structure of Polyurethane that is widely regarded as Polyurethane foam.
Polyurethane foam is known by many names across the market. Some of which you may be familiar with and are as follows:
- Construction foam
- Door assembling PU foam
- Gap filling PU foam
- High Resilience foam
- Heat insulation PU foam
- Insulation foam
- High density foam
- Montage PU foam
- Mounting PU foam
- OCF PU foam sealant
- One component PU foam
- Polyurethane PU foam
- Sound isolation PU foam
- Window assembling PU foam
All these names are derived from the variances in how it’s processed, or what it’s specifically used for, and other specific properties added during processing.
Meaning these different names, in general, imply a specific type, form of use, or other special properties added to polyurethane foam.
You might call these “blends” of foam, and each manufacturer can create their own blend – to achieve specific purposes.
How polyurethane foam is made
There is a lot of science behind how polyurethane foam is made. It’s a complex process that frankly, only people in the industry would understand or want to know more about.
If you do want to know more, I’m sure there are expert chemists and websites far better able to explain that part than me. So I’ll stick with a simple description.
Polyurethane foam is made by reacting compounds of polyols and diisocyanates. Both these compounds are derived from crude oil. Blending these with viscose and other formulated chemicals creates a reaction that produces polyurethane.
The basic process of making polyurethane foam will include a series of other additives to produce various quality PU foam products.
The additives that are usually included are based on the application required of the foam, i.e. based on what the PU foam will be eventually be intended for.
The different names listed above are given for polyurethane, based on these variants. And each variant provides a specific purpose or application in the foam world.
To provide some examples …below is a comparison photo of typical examples of open-cell soft, medium, and high-density foam. At first glance, they look largely the same, but at closer examination, you may be able to see that the cell structure becomes denser between soft and high.
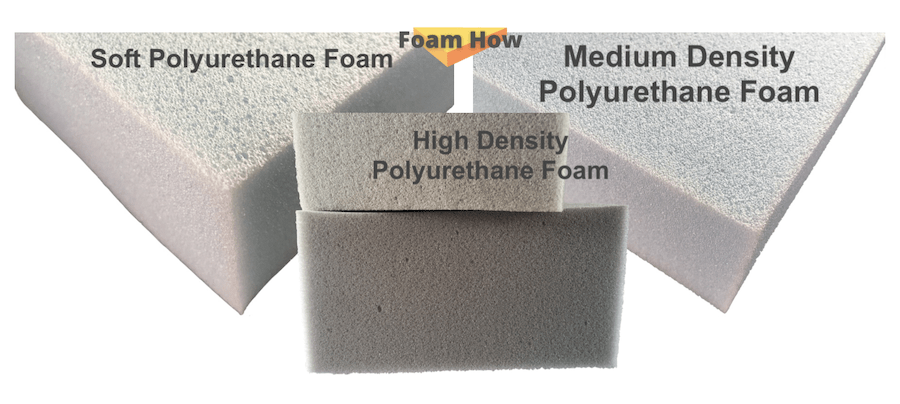
There are of course exceptions in polyurethane foam, one exception is High Resilience foam which is designed to be very dense. I have a separate article about High Resilience foam here. Another exception that you “might” be able to consider is Dry Fast foam.
Typical uses for polyurethane foam
Here are some of the typical environments in which you might find polyurethane foam.
- Lower quality mattress toppers
- Dog beds
- Packaging, shipping, and general filling
- Costumes and padding
- Furniture
Amazon options for Polyurethane foam
Features of polyurethane foam
There are good points and bad points about polyurethane foam, and here I’m focussing more on open-cell polyurethane foam. So let’s go through some of those features next.
Less-expensive
In general, PU foam is less expensive than other types of foam. This is why it’s been used for many different purposes, covering a wide range of industries.
The lower the quality – the less expensive it is. It’s this budget-friendly option that has made PU foam a quick and easy option for foam projects and products.
These days, PU foam is also used as a top layer for spring mattresses because of its affordability. Especially as there are denser and higher resilience PU foam that has come on to the market – at still an affordable price.
More recently the budget price aspect of polyurethane foam has even encouraged online mattress manufacturers to use it as a base layer in their mattresses.
Low to medium quality
When it comes to the quality of polyurethane foam, in general, it has always been considered a low to mid-range product, but …there are now some on the market that of a higher quality.
However, having said that, it is still more common to find lower-quality polyurethane foam than high-quality polyurethane foam.
The lower quality is, without doubt, the main reason polyurethane foam is less expensive than other foams on the market.
High-quality open-cell polyurethane foams that are available, such as High-Density Foam, or High Resilience foam, are made by using certain specific additives to the basic process during manufacture.
Generally, it’s easy to identify the quality of PU foam from its price; the lesser the price the lower the quality.
Low to medium density
Density and Firmness are very important aspects of foam, whether it’s open-cell or closed-cell. Generally, polyurethane foams have varying densities, depending on their chemical makeup and their intended use.
However, in general, most of them err on the side of lower density levels. This is even true of the high-density foam when compared to other types of foams. And the general rule is, the higher the density the longer the durability …and the greater the cost.
So low-density PU foam is more likely to degrade quicker, sometimes even within a year of use. Even high-density (closed cell) polyurethane foam, however, is still less dense than latex foam or memory foam.
This is why many PU foams degrade faster (short-durability) than even a decent quality latex foam. This low-density feature of polyurethane foam is what makes it easy to compress.
Low-density also means more lightweight. This lightweight actually helps international retailers save on shipping costs, and is one of the reasons why many online mattress retailers are moving towards the use of PU foam, despite its lower quality.
Soft texture and reasonable support
The best or perhaps the most appealing feature about polyurethane foam is that it has a soft texture.
This soft texture is what makes PU foam ideal or well known for use in mattress cushions, sofas, and most other forms of seating.
However, it’s the same soft texture that makes the foam collapse much quicker when pressure is applied.
Despite the soft texture, polyurethane foam can still provide a certain degree of support. But this is not the same type of firmness and consistent support that many other types of foams provide.
Besides, exposure to hazardous elements from the environment can collapse the foam to degrade the support and embedded structure faster.
Short life span
The low-quality and low density of polyurethane foam on its own reduce its durability and thereby contributes to a short life span.
On average the lifespan of Polyurethane foams lasts somewhere between 2 – 5 years, depending on the density. If you purchase higher quality PU foam products they will last longer than this average period.
Also, the short-life span of PU foams can be further shortened depending on how they’re used.
One main element that reduces the life span of PU foam is prolonged exposure to intense UV lights. UV lights can easily deform the foam.
This can result in corrupting the structure that foam is formed in. You can protect dried PU foam from hazardous lightings by covering or painting its surface.
Moreover, some fire-resistant foams can resist fire for some time. These types of foam can resist fire when it’s exposed to flame or while remaining in the place of fire. How long PU foam can resist fire varies, but it can generally be for up to 217 minutes.
Fewer certifications
Because polyurethane is so mass produced and widespread, it is less likely to carry any emission certifications that can assure customers of its credibility.
While some may provide certifications, they lack the credibility of independent third-party certifications such as eco-INSTITUT or Oeko-tex.
This is a standard that was specifically designed and administered by the PU industry itself.
While less credibility is common for many PU foam brands, those that have acceptable certifications provide better assurance of quality and safety.
I’ve narrowed down some of the options you might want to consider for foam on Amazon below..
Amazon options for Polyurethane foam
Technical specifications
| Polyurethane Foam | |
|---|---|
| Quality | Low |
| Weight (lb per cubic ft) | 1.2 – 2.0 lb |
| Structure | Open Cell |
| Density (range 1.0 – 6.0) | 1.2 – 1.9 (12 – 19) |
| Firmness (ILD) | 15 – 60 (from plush to super firm) |
| Lifespan | 2-5 years |
| Colors | White or Beige |
| Applications | Lower quality mattress toppers, Dog beds, Packaging, Shipping, and general filling, Costumes and padding, Furniture |
To finish…
I hope this has provided a good overview on the question of what is polyurethane foam. Why not download my free quick reference guide on types of foams.
